You are responsible for any damage plants cause to nearby buildings, footpaths, underground pipes and other structures. Following these guidelines can reduce vegetation management issues in the future.
Avoid damage from roots
Plant root systems can cause blockages, cause overflows, and flooding, disrupting services to the community and involving costly repairs. They often extend into stormwater, sewage and water pipes in search of food and nutrients.
You can avoid damage by choosing appropriate plants (with suitable root systems) and ensuring plantings are a suitable distance from assets. You can also use root barriers. A root barrier is a tough material liner wrapped around the plant’s base when it is planted, which restricts the root system as the plant grows. Vegetation should also be planted in such a way to account for future growth.
Your local nursery will have information about suitable products.
For this guide, we have categorised vegetation into common forms:
- Mown Grass: up to 30cm in height
- Ground cover/Sedges: up to 1.5m in height
- Shrubs: 1.5m–4m high
- Trees: 4m and above
The form of vegetation is generally indicative of its root system; however, some species may have particularly vigorous root systems. When choosing an appropriate species it is important to consider the typical growth habits of the species and its suitability to the site. For more information regarding suitable species please contact your local council, nursery or Landcare group.
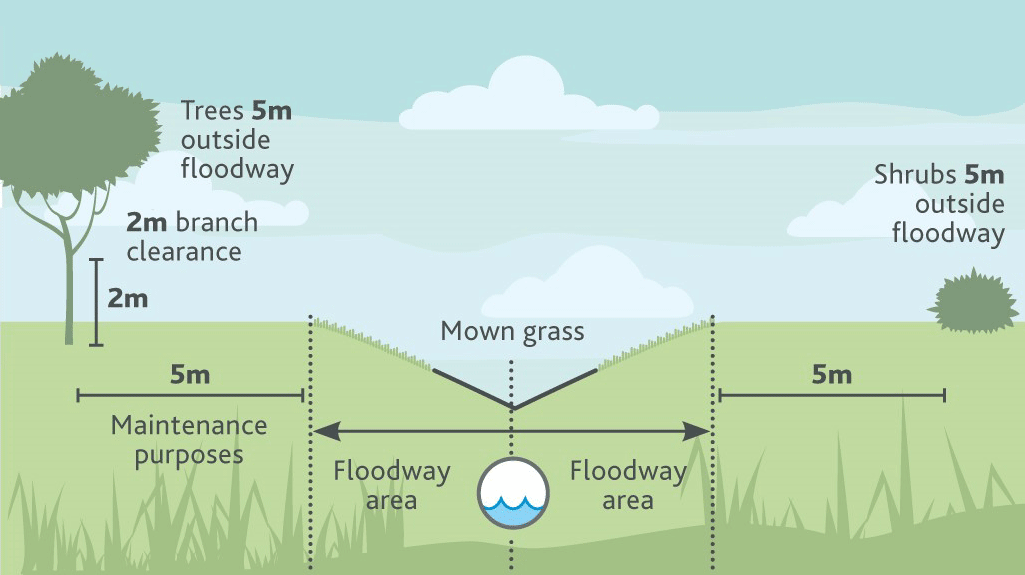
Floodways
Inappropriate planting or landscaping in floodways can obstruct water flow and increase flooding.
When planting in a floodway, within an overland flow path, ensure:
- Trees, shrubs and ground cover are 5m outside the floodway area
- Tree branches have a 2m clearance
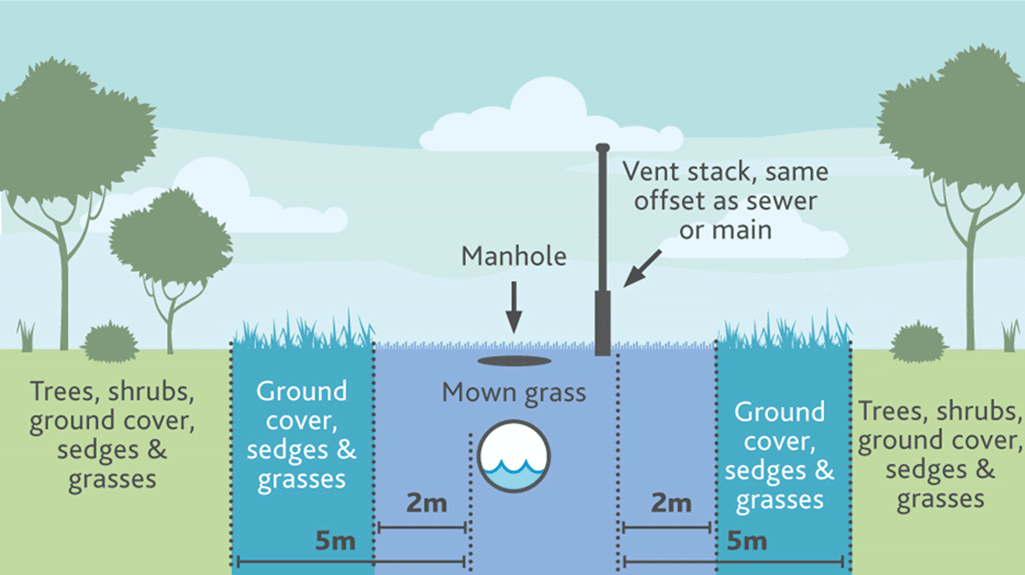
Underground pipes, manholes or vent stacks
Drains, sewers and water mains can become blocked and damaged by tree roots, disrupting services to the community and involving costly repairs. Vegetation can block access to critical maintenance points, such as maintenance holes and vent pipes.
As shown in diagram 2:
- Only mown grass should directly over or around an asset
- Ground cover species should be at least 2m from the edge of assets
- Trees and shrubs should be planted so that the mature canopy and roots are at least 5m from the edge of assets
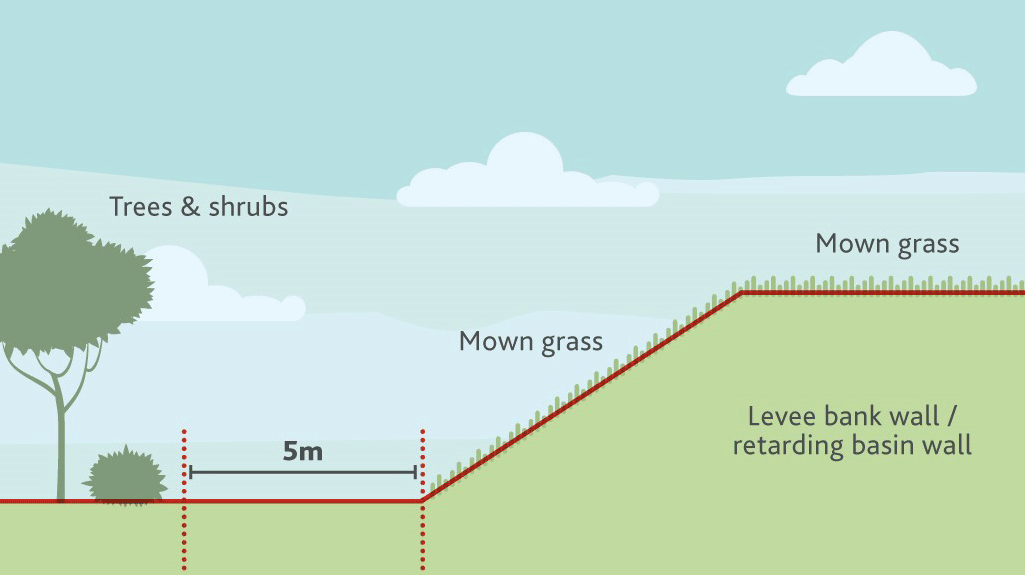
Levee banks
Vegetation can weaken levee banks and dam walls, potentially causing the bank to leak or collapse. Trees, shrubs and ground cover species should be planted at least 5m away from the toe of the wall.
Planting guideline
Apply online
Your feedback
Contact Asset Services for plant recommendations or hydraulic investigation to assess the impact of planting:
-
call 131 722